Windows Filtering Platform
Purpose
Windows Filtering Platform (WFP) is a set of API and system services that provide a platform for creating network filtering applications. The WFP API allows developers to write code that interacts with the packet processing that takes place at several layers in the networking stack of the operating system. Network data can be filtered and also modified before it reaches its destination.
By providing a simpler development platform, WFP is designed to replace previous packet filtering technologies such as Transport Driver Interface (TDI) filters, Network Driver Interface Specification (NDIS) filters, and Winsock Layered Service Providers (LSP). Starting in Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista, the firewall hook and the filter hook drivers are not available; applications that were using these drivers should use WFP instead.
With the WFP API, developers can implement firewalls, intrusion detection systems, antivirus programs, network monitoring tools, and parental controls. WFP integrates with and provides support for firewall features such as authenticated communication and dynamic firewall configuration based on applications’ use of sockets API (application-based policy). WFP also provides infrastructure for IPsec policy management, change notifications, network diagnostics, and stateful filtering.
Windows Filtering Platform is a development platform and not a firewall itself. The firewall application that is built into Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, and later operating systems Windows Firewall with Advanced Security (WFAS) is implemented using WFP. Therefore, applications developed with the WFP API or the WFAS API use the common filtering arbitration logic that is built into WFP.
The WFP API consists of a user-mode API and a kernel-mode API. This section provides an overview of the entire WFP and describes in detail only the user-mode portion of the WFP API. For a detailed description of the kernel-mode WFP API, see the Windows Driver Kit online help.
Developer audience
The Windows Filtering Platform API is designed for use by programmers using C/C++ development software. Programmers should be familiar with networking concepts and design of systems using user-mode and kernel-mode components.
Run-time requirements
The Windows Filtering Platform is supported on clients running Windows Vista and later, and on servers running Windows Server 2008 and later. For information about the run-time requirements for a specific programming element, see the Requirements section of the reference page for that element.
In this section
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| What’s New in Windows Filtering Platform | Information on new features and APIs in Windows Filtering Platform. |
| About Windows Filtering Platform | An overview of Windows Filtering Platform. |
| Using Windows Filtering Platform | Example code using the Windows Filtering Platform API. |
| Windows Filtering Platform API Reference | Documentation for the Windows Filtering Platform functions, structures, and constants. |
Additional resources
To ask questions and have discussions about using the WFP API, visit the Windows Filtering Platform Forum.
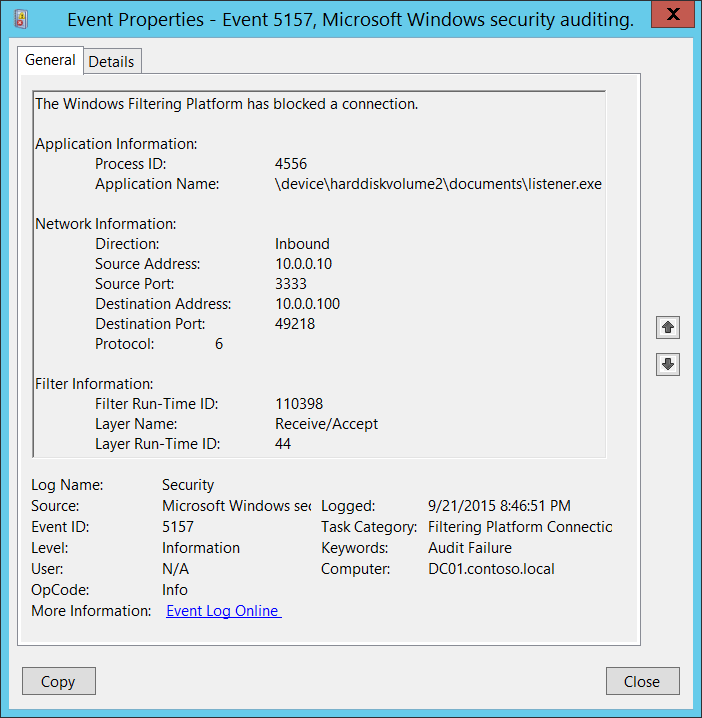
5157 (F): платформа фильтрации Windows заблокировала подключение. 5157(F): The Windows Filtering Platform has blocked a connection.
Относится к: Applies to
- Windows 10; Windows 10
- Windows Server2016 Windows Server 2016
Описание события: Event Description:
Это событие генерируется, когда платформа фильтрации Windows заблокировала соединение. This event generates when Windows Filtering Platform has blocked a connection.
Note Примечание Рекомендации можно найти в статье рекомендации по мониторингу безопасности для этого события. Note For recommendations, see Security Monitoring Recommendations for this event.
XML-код события: Event XML:
Обязательные роли сервера: Ничего. Required Server Roles: None.
Минимальная версия ОС: Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista. Minimum OS Version: Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista.
Версии событий: до. Event Versions: 0.
Описания полей: Field Descriptions:
Сведения о приложении: Application Information:
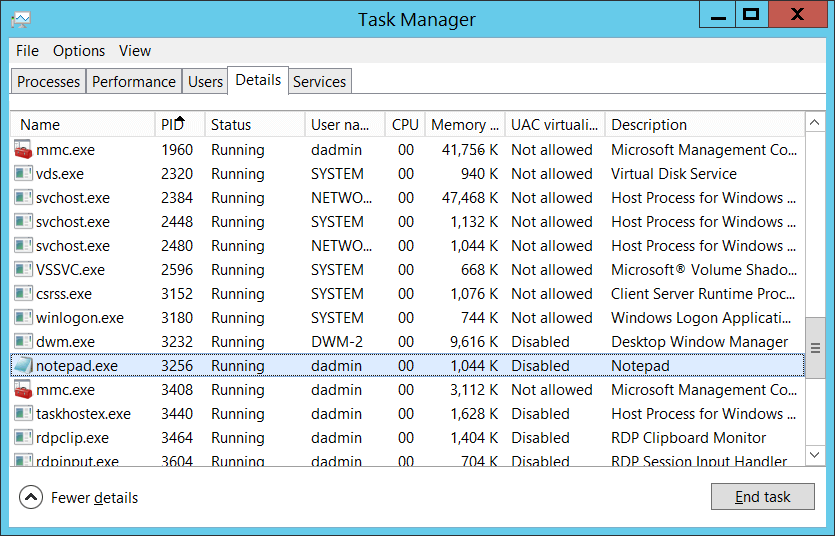
Process ID \ [тип = указатель ]: ШЕСТНАДЦАТЕРИЧный идентификатор процесса, который попытался создать соединение. Process ID [Type = Pointer]: hexadecimal Process ID of the process that attempted to create the connection. Идентификатор процесса (PID) — это число, используемое операционной системой для уникальной идентификации активного процесса. Process ID (PID) is a number used by the operating system to uniquely identify an active process. Чтобы просмотреть PID для определенного процесса, например с помощью диспетчера задач (вкладка «сведения», столбец PID), выполните указанные ниже действия. To see the PID for a specific process you can, for example, use Task Manager (Details tab, PID column):
Если преобразовать шестнадцатеричное значение в десятичное, его можно сравнить с значениями в диспетчере задач. If you convert the hexadecimal value to decimal, you can compare it to the values in Task Manager.
Вы также можете сопоставить этот идентификатор процесса с ИДЕНТИФИКАТОРом процесса в других событиях, например «4688: создан новый процесс» Information\New Process ID процесса. You can also correlate this process ID with a process ID in other events, for example, “4688: A new process has been created” Process Information\New Process ID.
Имя приложения \ [тип = UnicodeString ]: полный путь и имя исполняемого файла для процесса. Application Name [Type = UnicodeString]: full path and the name of the executable for the process.
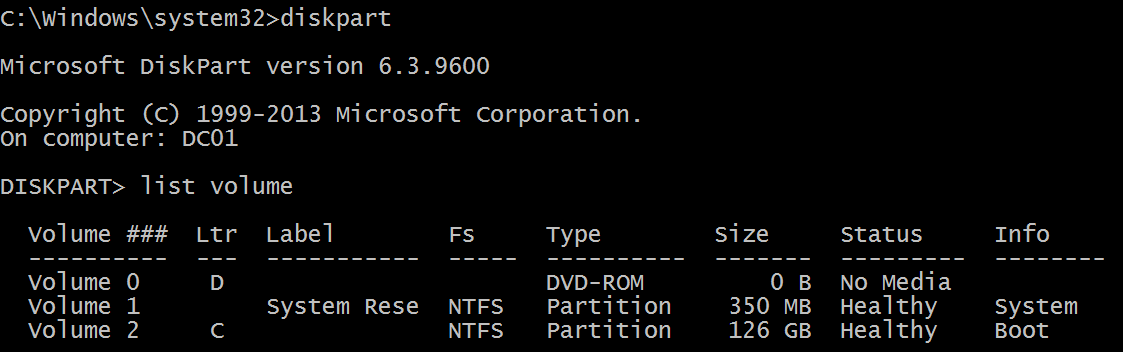
Логический диск отображается в формате \device\harddiskvolume\ #. Logical disk is displayed in format \device\harddiskvolume#. С помощью средства DiskPart вы можете получать номера всех локальных томов. You can get all local volume numbers by using diskpart utility. Для получения номеров тома с помощью DiskPart используется команда «List Volume»: The command to get volume numbers using diskpart is “list volume”:
Сведения о сети: Network Information:
Направление \ [тип = UnicodeString ]: направление заблокированного подключения. Direction [Type = UnicodeString]: direction of blocked connection.
Входящее – для входящих подключений. Inbound – for inbound connections.
Исходящие — для несвязанных подключений. Outbound – for unbound connections.
Исходный адрес \ [тип = UnicodeString ]: локальный IP-адрес, на который приложение получало соединение. Source Address [Type = UnicodeString]: local IP address on which application received the connection.
IPv4-адрес IPv4 Address
IPv6-адрес IPv6 Address
::-все IP-адреса в формате IPv6 :: — all IP addresses in IPv6 format
0.0.0.0 — все IP-адреса в формате IPv4 0.0.0.0 — all IP addresses in IPv4 format
127.0.0.1. 1-localhost 127.0.0.1 , ::1 — localhost
Исходный порт \ [тип = UnicodeString ]: номер порта, на котором приложение получило соединение. Source Port [Type = UnicodeString]: port number on which application received the connection.
Адрес назначения \ [Type = UnicodeString ]: IP-адрес, с которого было получено или инициировано соединение. Destination Address [Type = UnicodeString]: IP address from which connection was received or initiated.
IPv4-адрес IPv4 Address
IPv6-адрес IPv6 Address
::-все IP-адреса в формате IPv6 :: — all IP addresses in IPv6 format
0.0.0.0 — все IP-адреса в формате IPv4 0.0.0.0 — all IP addresses in IPv4 format
127.0.0.1. 1-localhost 127.0.0.1 , ::1 — localhost
Порт назначения \ [Type = UnicodeString ]: номер порта, который использовался на удаленном компьютере для запуска подключения. Destination Port [Type = UnicodeString]: port number which was used from remote machine to initiate connection.
Protocol \ [тип = UInt32 ]: число использованных протоколов. Protocol [Type = UInt32]: number of protocol which was used.
| Обслуживание Service | Номер протокола Protocol Number |
|---|---|
| Протокол управляющих сообщений в Интернете (ICMP) Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) | 1,1 1 |
| Протокол управления передачей данных (TCP) Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) | 152 6 |
| UDP (User Datagram Protocol) User Datagram Protocol (UDP) | 18 17 |
| Общая Инкапсуляция маршрутизации (PPTP-данные по GRE) General Routing Encapsulation (PPTP data over GRE) | 47 47 |
| Заголовок Authentication (AH) IPSec Authentication Header (AH) IPSec | 51 51 |
| IPSec (ESP) (полезные данные безопасности) Encapsulation Security Payload (ESP) IPSec | 50 50 |
| Протокол для внешней шлюза (EGP) Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) | No8 8 |
| Протокол шлюза (GGP) Gateway-Gateway Protocol (GGP) | Трехконтактный 3 |
| Протокол наблюдения за узлом (HMP) Host Monitoring Protocol (HMP) | средняя 20 |
| Протокол IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) | 88 88 |
| Удаленный виртуальный диск MIT (RVD) MIT Remote Virtual Disk (RVD) | 66 66 |
| OSPF — открытие кратчайшего пути сначала OSPF Open Shortest Path First | 89 89 |
| Протокол универсальных пакетов PARC (PUP) PARC Universal Packet Protocol (PUP) | 12 12 |
| Надежный протокол датаграмм (RDP) Reliable Datagram Protocol (RDP) | отображал 27 |
| QoS по протоколу резервирования (RSVP) Reservation Protocol (RSVP) QoS | 46 46 |
Сведения о фильтре: Filter Information:
Filter код времени выполнения \ [тип = UInt64 ]: уникальный идентификатор фильтра, который блокировал соединение. Filter Run-Time ID [Type = UInt64]: unique filter ID which blocked the connection.
Чтобы найти определенный фильтр платформы фильтрации Windows по ИДЕНТИФИКАТОРу, необходимо выполнить следующую команду: netsh wfp show filters. To find specific Windows Filtering Platform filter by ID you need to execute the following command: netsh wfp show filters. В результате этой команды будет создано filters.xml файл. As result of this command filters.xml file will be generated. Вам нужно открыть этот файл и найти определенную подстроку с обязательным идентификатором фильтра (** filterId**),** например: You need to open this file and find specific substring with required filter ID ( ),** for example:
Имя слоя \ [Type = UnicodeString ]: имя слоя принудительного применения уровня приложения . Layer Name [Type = UnicodeString]: Application Layer Enforcement layer name.
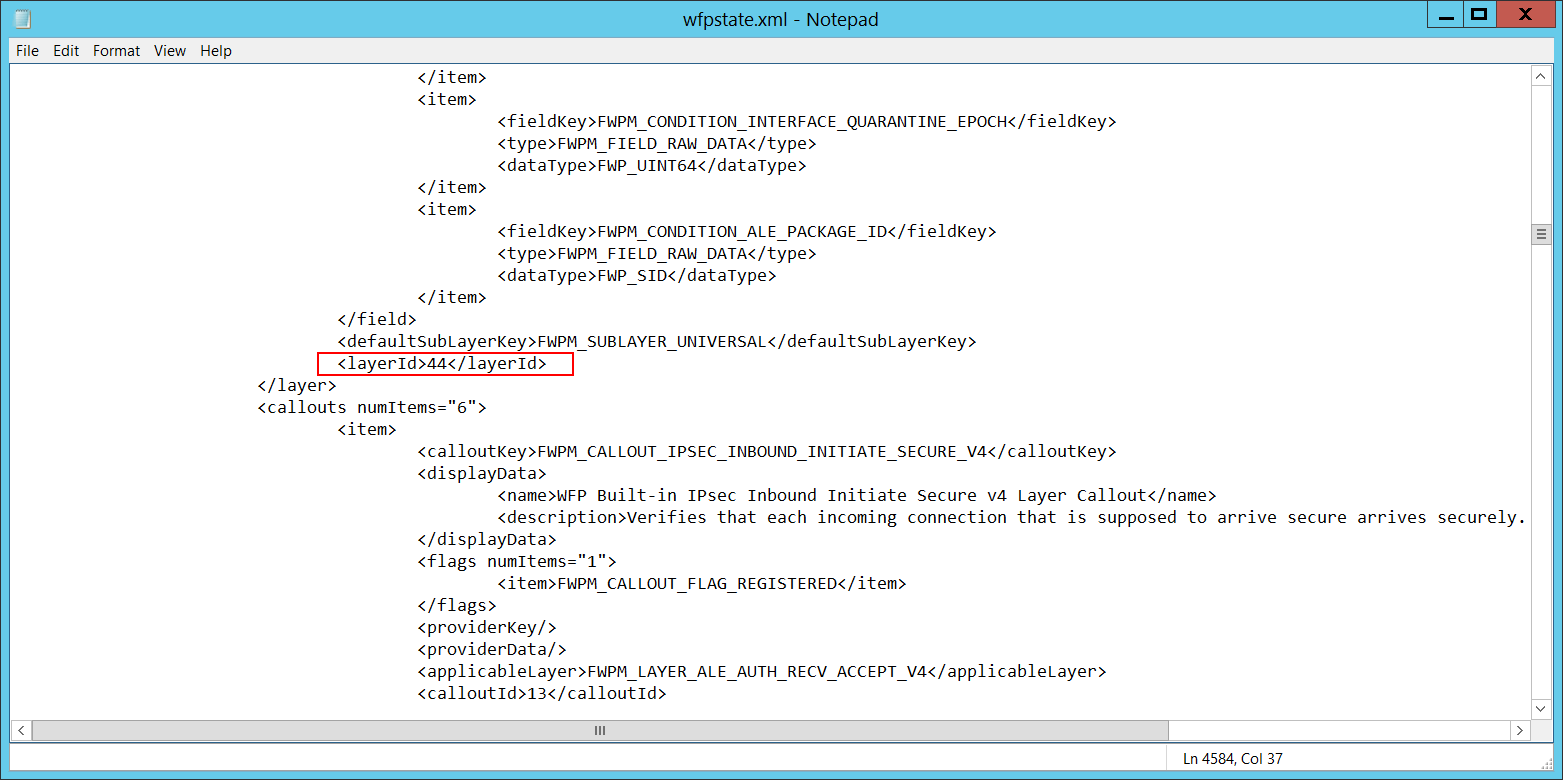
Код выполнения уровня \ [тип = UInt64 ]: идентификатор уровня платформы фильтрации Windows. Layer Run-Time ID [Type = UInt64]: Windows Filtering Platform layer identifier. Чтобы найти определенный идентификатор уровня платформы фильтрации Windows, необходимо выполнить следующую команду: netsh wfp show state (состояние). To find specific Windows Filtering Platform layer ID you need to execute the following command: netsh wfp show state. В результате этой команды будет создано wfpstate.xml файл. As result of this command wfpstate.xml file will be generated. Вам нужно открыть этот файл и найти определенную подстроку с требуемым идентификатором уровня (** layerId**),** например: You need to open this file and find specific substring with required layer ID ( ),** for example:
Рекомендации по мониторингу безопасности Security Monitoring Recommendations
Для 5157 (F): платформа фильтрации Windows заблокировала подключение. For 5157(F): The Windows Filtering Platform has blocked a connection.
Если у вас есть предопределенное приложение, которое должно использоваться для выполнения операции, о которой сообщило данное событие, наблюдайте за событиями «приложение» и не эквивалентно определенному приложению. If you have a pre-defined application which should be used to perform the operation that was reported by this event, monitor events with “Application” not equal to your defined application.
Вы можете следить за тем, чтоприложениене находится в стандартной папке (например, не в каталог system32 или файлы программ) или находится в папке с ограниченным доступом (например, временные файлы Интернета). You can monitor to see if “Application” is not in a standard folder (for example, not in System32 or Program Files) or is in a restricted folder (for example, Temporary Internet Files).
Если у вас есть предварительно определенный список ограниченных подстрок или слов в именах приложений (например, «mimikatz» или «cain.exe«), проверьте эти подстроки в «Application«. If you have a pre-defined list of restricted substrings or words in application names (for example, “mimikatz” or “cain.exe”), check for these substrings in “Application.”
Убедитесь, что «исходный адрес» — один из адресов, назначенных компьютеру. Check that “Source Address” is one of the addresses assigned to the computer.
Если компьютер или устройство не должны иметь доступ к Интернету или содержит только те приложения, которые не подключены к Интернету, наблюдайте за событиями 5157 , в которыхадрес назначения является IP-адресом из Интернета (не из диапазонов частных IP-адресов). If the` computer or device should not have access to the Internet, or contains only applications that don’t connect to the Internet, monitor for 5157 events where “Destination Address” is an IP address from the Internet (not from private IP ranges).
Если вы знаете, что компьютеру не следует общаться или общаться с определенными IP-адресами сети, проследите за этими адресами в разделе «адрес назначения«. « If you know that the computer should never contact or be contacted by certain network IP addresses, monitor for these addresses in “Destination Address.”
Если у вас есть список разрешенных IP-адресов, к которым должен быть подключен компьютер или устройство, проследите за IP-адресами в разделе «конечный адрес» , который не входит в список разрешений. If you have an allow list of IP addresses that the computer or device is expected to contact or be contacted by, monitor for IP addresses in “Destination Address” that are not in the allow list.
Если вам нужно наблюдать за всеми входящими подключениями к определенному локальному порту, проследите за событиями 5157 с помощью этого «исходного порта«. « If you need to monitor all inbound connections to a specific local port, monitor for 5157 events with that “Source Port.”
Отслеживайте все соединения с помощью «номера протокола» , которое не является типичным для этого устройства или compter, например, что угодно, кроме 1, 6 или 17. Monitor for all connections with a “Protocol Number” that is not typical for this device or compter, for example, anything other than 1, 6, or 17.
Если на компьютере с параметром «адрес назначения» необходимо всегда использоватьопределенный порт назначения,****проследите за любым другимпортом назначения. If the computer’s communication with “Destination Address” should always use a specific “Destination Port,” monitor for any other “Destination Port.”