Windows Server 2003
| Windows Server 2003 | |
| Разработчик | Microsoft Corporation |
|---|---|
| Семейство ОС | Windows NT |
| Первый выпуск | 24 апреля 2003 [1] |
| Последняя версия | 2003 SP2 (5.2.3790.3959) (13 марта 2007 года) |
| Тип ядра | Гибридное ядро |
| Лицензия | Microsoft EULA |
| Состояние | Общая поддержка прекращена 13 июля 2010 года; расширенная — 14 июля 2015 [2] |
| Предыдущая | Windows 2000 |
| Следующая | Windows Server 2003 R2 [d] и Windows Server 2008 |
| Веб-сайт | (Архив) |
Windows Server 2003 (кодовое название при разработке — Whistler Server, внутренняя версия — Windows NT 5.2) — операционная система семейства Windows NT от компании Microsoft, предназначенная для работы на серверах. Она была выпущена 24 апреля 2003 года [3] .
Windows Server 2003 является новой версией Windows 2000 Server и серверным вариантом операционной системы Windows XP. Изначально Microsoft планировала назвать этот продукт «Windows .NET Server» с целью продвижения своей новой платформы Microsoft .NET. Однако впоследствии это название было отброшено, чтобы не вызвать неправильного представления о .NET на рынке программного обеспечения.
Содержание
Новые функции системы
Windows Server 2003 в основном развивает функции, заложенные в предыдущей версии системы — Windows 2000 Server. На это указывала и версия NT 5.2 ядра системы (NT 5.0 для Windows 2000). Ниже приведены некоторые из наиболее заметных изменений по сравнению с Windows 2000 Server.
Поддержка .NET
Windows Server 2003 — первая из операционных систем Microsoft, которая поставляется с предустановленной программной платформой .NET Framework. Это позволяет операционной системе выступать в роли сервера приложений для платформы Microsoft .NET без установки дополнительного программного обеспечения.
Улучшения Active Directory
Windows Server 2003 включает в себя следующие улучшения для Active Directory — службы каталогов, впервые появившейся в Windows 2000:
- Возможность переименования домена Active Directory после его развёртывания.
- Упрощение изменения схемы Active Directory — например, отключения атрибутов и классов.
- Улучшенный пользовательский интерфейс для управления каталогом (стало возможно, например, перемещать объекты путём их перетаскивания и одновременно изменять свойства нескольких объектов).
- Улучшенные средства управления групповой политикой, включая программу Group Policy Management Console.
IIS 6.0
В составе Windows Server 2003 распространяется версия 6.0 служб Internet Information Services, архитектура которой существенно отличается от архитектуры служб IIS 5.0, доступных в Windows 2000. В частности, для повышения стабильности стало возможным изолировать приложения друг от друга в отдельных процессах без снижения производительности. Также был создан новый драйвер HTTP.sys для обработки запросов по протоколу HTTP. Этот драйвер работает в режиме ядра, в результате чего обработка запросов ускоряется.
Безопасность
По заявлениям Microsoft, в Windows Server 2003 большое внимание было уделено системе безопасности [ источник не указан 820 дней ] . В частности, система теперь устанавливается в максимально ограниченном виде, без каких-либо дополнительных служб, что уменьшает поверхность атаки. В Windows Server 2003 также включён программный межсетевой экран Internet Connection Firewall. Впоследствии к системе был выпущен пакет обновления, который полностью сосредоточен на повышении безопасности системы и включает несколько дополнительных функций для защиты от атак. Согласно американскому стандарту безопасности Trusted Computer System Evaluation Criteria (TCSEC), система Windows Server 2003 относится к классу безопасности C2 — Controlled Access Protection.
Прочее
В Windows Server 2003 впервые появилась служба теневого копирования тома (англ. Volume Shadow Copy Service ), которая автоматически сохраняет старые версии пользовательских файлов, позволяя при необходимости вернуться к предыдущей версии того или иного документа. Работа с теневыми копиями возможна только при установленном «клиенте теневых копий» на ПК пользователя, документы которого необходимо восстановить.
Также в данной версии системы был расширен набор утилит администрирования (dsadd, dsget, dsmod и др.), вызываемых из командной строки, что упрощает автоматизацию управления системой.
Введено новое понятие — «роли», на них основано управление сервером. Проще говоря, чтобы получить файл-сервер, необходимо добавить роль — «файл-сервер».
Поддержка оборудования
Windows Server 2003, Standard Edition поддерживает 4 центральных процессора и до 4 Гбайт оперативной памяти. 64-разрядная версия Standard Edition поддерживают до 32 Гбайт оперативной памяти.
Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition поддерживает до 32 Гбайт оперативной памяти на процессорах х86 (оперативная память более 4Гбайт может использоваться только при включенной функции Physical Address Extension [4] , до 64 Гбайт оперативной памяти на процессорах Itanium и до 8 центральных процессоров. В ней также поддерживаются 64-разрядные процессоры Intel Itanium, оперативная память с возможностью «горячей» замены и неоднородный доступ к памяти (NUMA).
Windows Server 2003 Datacenter Edition способна работать с бо́льшими объёмами оперативной памяти — до 64 Гбайт на процессорах х86 (для доступности более 4 Гбайт также необходимо включение PAE [4] ) и до 128 Гбайт на процессорах Itanium. Минимальное количество процессоров для работы Datacenter Edition — 8, максимальное — 32.
Издания
Windows Server 2003 доступен в четырёх основных изданиях, каждое из которых ориентировано на определённый сектор рынка.
Все эти издания, за исключением Web Edition, доступны также в 64-разрядных вариантах (AMD64 и IA-64). Включение поддержки 64-разрядных процессоров даёт системам возможность использовать большее адресное пространство и увеличивает их производительность.
- Web Edition — серверная система, оптимизированная для Web- служб и Web- узлов (издание для World Wide Web) представляет собой «облегчённую» версию Windows Server 2003 специально для использования на веб-серверах. Это издание не способно выполнять функции контроллера домена и не поддерживает некоторые другие важные возможности прочих изданий, но содержит службы IIS и стоит значительно дешевле. Поддерживает до 2 гигабайт [5] оперативной памяти и до четырёх процессоров на компьютер.
- Standard Edition (стандартное издание) ориентировано на малый и средний бизнес. Оно содержит все основные возможности Windows Server 2003, но в нём недоступны некоторые функции, которые, по мнению Microsoft, необходимы только крупным предприятиям. Поддерживает до 4 гигабайт [5] оперативной памяти и до четырёх процессоров на компьютер.
- Enterprise Edition (издание для предприятий) ориентировано на средний и крупный бизнес. В дополнение к возможностям Standard Edition, оно позволяет использовать больший объём оперативной памяти (до 32 гигабайт [5] оперативной памяти) и SMP на 8 процессоров (Standard Edition поддерживает лишь 4). Это издание также поддерживает кластеризацию и добавление оперативной памяти «на лету».
- Datacenter Edition (издание для центров данных) ориентировано на использование в крупных предприятиях при большой нагрузке. Windows Server 2003, Datacenter Edition может одновременно поддерживать в определённых ситуациях больше 10000 пользователей и кластеры, содержащие до восьми узлов. Эта система поддерживает до 64 процессоров и 128 гигабайт [5] оперативной памяти.
Windows Compute Cluster Server 2003
Windows Compute Cluster Server 2003 (CCS), выпущенный в июне 2006 года разработан для высокотехнологичных приложений, которые требуют кластерных вычислений. Издание разработано для развертывания на множестве компьютеров, которые собираются в кластер для достижения мощностей суперкомпьютера. Каждый кластер на Windows Compute Cluster Server состоит из одной или нескольких управляющих машин, распределяющих задания и нескольких подчиненных машин, выполняющих основную работу. Computer Cluster Server использует the Microsoft Messaging Passing Interface v2 (MS-MPI ( англ. ) ) для связи между исполняющими машинами в сети-кластере. Он связывает части кластера вместе мощным надпроцессовым механизмом. API состоит из более чем 160 функций. MS MPI был разработан как совместимым с open source интерфейсом MPI2, который широко используется в высокопроизводительных вычислениях. За некоторыми исключениями по соображениям безопасности MS MPI покрывает функциональность MPI2 за исключением возможностей динамического порождения процессов.
Продукты, в которых используется Windows Server 2003
Некоторые другие продукты Microsoft также включают в себя Windows Server 2003 в качестве основы:
- Microsoft Small Business Server 2003 — продукт для малого бизнеса, содержащий в себе всё необходимое (по мнению Microsoft) для первого сервера небольшого предприятия. В дополнение к Windows Server 2003, этот пакет содержит Microsoft SQL Server, Microsoft ISA Server и некоторые другие продукты, а также упрощённые средства управления. Версия Windows Server 2003, входящая в этот пакет, имеет некоторые ограничения, в основном связанные со службой Active Directory (например, она не может поддерживать более 75 пользователей).
- Microsoft Windows Storage Server 2003 — выделенный файловый сервер для хранения большого количества данных.
Обновления
Service Pack 1
30 марта 2005 года Microsoft выпустила пакет обновления 1 (SP1) для Windows Server 2003. Этот пакет включает в себя различные улучшения системы безопасности, в том числе:
- Security Configuration Wizard (мастер конфигурации безопасности) — средство, предназначенное для уменьшения поверхности атаки серверов. SCW анализирует роли, выполняемые сервером, и отключает ненужные службы, а также включает некоторые дополнительные средства безопасности.
- Windows Firewall — новая версия программного межсетевого экрана, замена Internet Connection Firewall.
- Post-Setup Security Updates — средство, снижающее уязвимость только что установленной копии Windows Server 2003 путём блокировки всех сетевых портов до установки обновлений безопасности с веб-сайта Microsoft.
- Аутентификация и шифрование для службы Windows Terminal Services с применением SSL[6]
Windows Server 2003 R2
6 декабря 2005 года Microsoft выпустила новую версию Windows Server 2003, официально называемую R2 (от англ. Release 2 — «выпуск 2»). Согласно заявлениям Microsoft, эта версия включает в себя существенные улучшения в следующих областях:
- управление серверами подразделений;
- управление учётными записями и доступом;
- управление хранилищами;
- веб-приложения;
- виртуальные серверы.
Service Pack 2
Service Pack 2 для Windows Server 2003 был выпущен 13 марта 2007 года [7] , хотя первоначально его выпуск был запланирован на первую половину 2006 года [8]
Microsoft характеризует Service Pack 2 как стандартный выпуск пакета обновления, содержащий ранее выпущенные обновления безопасности, хотфиксы, улучшения надежности и производительности. Помимо этого, Service Pack 2 содержит в себе Microsoft Management Console 3.0, Windows Deployment Services (который заменил Remote Installation Services), поддержку WPA2 и добавление функциональности в IPSec и MSConfig. Service Pack 2 также содержит возможности Windows Server 2003 Scalable Networking Pack (SNP), [9] , позволяющие сделать аппаратное ускорение обработки сетевых пакетов.
Windows Server 2003
Windows Server 2003
Developer
OS family
Working state
Source model
Final release
Marketing target
Default user interface
Licensing
Released to manufacturing
General availability
Kernel type
Preceded by
Succeeded by
Website
Support status

Microsoft Windows Server 2003 logo screen.
Windows Server 2003 (codenamed Whistler Server) is the name of Microsoft’s line of server operating systems. It was introduced in April 2003 as the successor to Windows Server 2000, and is considered by Microsoft to be the cornerstone of their Windows Server System line of business server products. Windows Server 2003 was unsupported (extended-ly) since 2015. It has since been succeeded by Windows Server 2003 R2.
Contents
Overview
Released on April 24, 2003, Windows Server 2003 (which carries the version number 5.2) is the follow-up to Windows Server 2000, incorporating compatibility and other features from Windows XP. Unlike Windows Server 2000, Windows Server 2003’s default install has none of the server components enabled, to reduce the attack surface of new machines. Windows Server 2003 includes compatibility modes to allow older applications to run with greater stability. It was made more compatible with Windows NT 4.0 domain-based networking. Incorporating and upgrading a Windows NT 4.0 domain to Windows 2000 was considered difficult and time consuming, and generally was considered an all or nothing upgrade particularly when dealing with Active Directory. Windows Server 2003 brought in enhanced Active Directory compatibility, and better deployment support, to ease the transition from Windows NT 4.0 to Windows Server 2003 and Windows XP Professional.
Significant enhancements have been made to various services such as the IIS web server (which was almost completely re-written to improve performance and security), Distributed File System (which now supports hosting multiple DFS roots on a single server), Terminal Server, Active Directory, Print Server, and a number of other areas. Windows Server 2003 was also the first operating system released by Microsoft after the announcement of their Trustworthy Computing initiative, and as a result, contains a number of improvements to security defaults and practices.
The product went through several name changes during the course of development. When first introduced to technical beta testers in mid-2000, it was known by its codename, «Whistler Server»; it then changed to «Windows Server 2002» for a brief time in mid-2001, before being renamed «Windows .NET Server» as part of Microsoft’s effort to promote their new integrated enterprise and development framework, Microsoft .NET. However, due to fears of confusing the market about what «.NET» represents and responding to criticism, Microsoft removed .NET from the name during the Release Candidate stage in late 2002. This allowed the name .NET to exclusively apply to the .NET Framework, as previously it had appeared that .NET was just a tag for a generation of Microsoft products.
In 2005, Microsoft announced Windows Longhorn Server as the next major version of Windows Server after Windows Server 2003, with a targeted release date of the first half of 2007.
Notable features
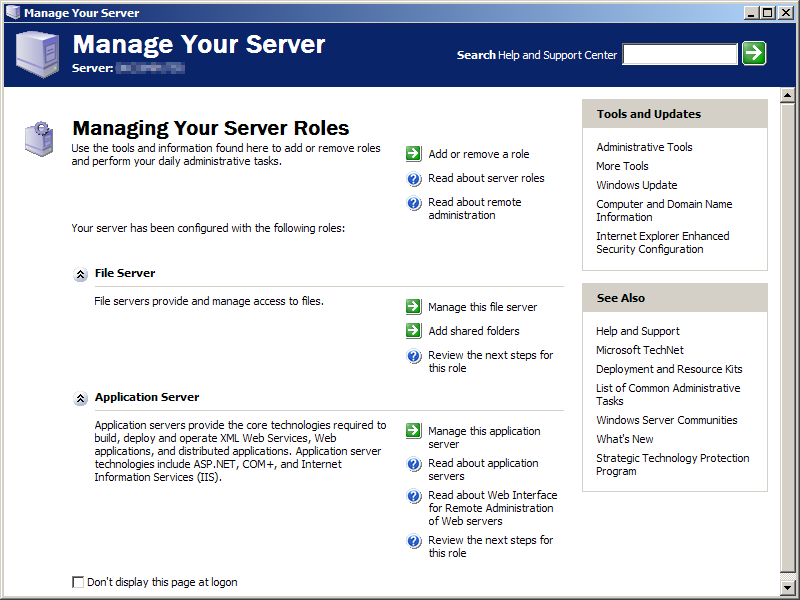
Manage Your Server
- Most versions of Windows Server include Terminal Services support (using the Remote Desktop Protocol), enabling multiple simultaneous remote graphical logins. This enables thin client computing on the windows platform, where all applications run remotely on the server. This feature was first introduced with a special «Terminal Server Edition» of Windows NT Server 4.0, but became more important when made a standard part of Windows 2000.
- Internet Information Services (IIS) v6.0 — again, versions of IIS were available on Windows 2000 and earlier, but IIS is improved significantly in Windows Server 2003.
- Active Directory — like Terminal Services, significantly improved since Windows 2000
- Increased default security over previous versions, due to the built-in firewall and most services being disabled by default.
- Message Queuing — significantly improved since Windows 2000
- Manage Your Server — a role management administrative tool that allows an administrator to choose what functionality the server should provide.
Improvements
There are a number of improvements from Windows Server 2000, notably:
- Improvements to Active Directory (such as the ability to deactivate classes from the schema, or to run multiple instances of the directory server (ADAM))
- Improvements to Group Policy handling and administration
- Improved disk management including the ability to backup from shadows of files, allowing the backup of open files.
- Improved scripting and command line tools, which are part of Microsoft’s initiative to bring a complete command shell to the next version of Windows.
- Support for a hardware-based «watchdog timer», which can restart the server if the operating system does not respond within a certain amount of time.
Service Pack 1
On March 30 2005, Microsoft released Service Pack 1 for Windows Server 2003. Among the improvements are many of the same updates that were provided to Windows XP users with Service Pack 2. Features that are added with Service Pack 1 include:
- Security Configuration Wizard: A tool that allows administrators to more easily research, and make changes to security policies. [1]
- Hot Patching: This feature is set to extend Windows Server 2003 ability to take DLL, Driver, and non-kernel patches without a reboot.
- IIS 6.0 Metabase Auditing: Allowing the tracking of metabase edits. [2]
- Windows Firewall: Brings many of the improvements from Windows XP Service Pack 2 to Windows Server 2003, also with the Security Configuration Wizard, it allows administrators to more easily manage the incoming open ports, as it will automatically detect and select default roles.
- Other networking improvements include support for Wireless Provisioning Services, better IPv6 support, and new protections against TCP SYN attacks. [3]
- Post-Setup Security Updates: A default mode that is turned on, when a Service Pack 1 server is first booted up after installation. It configures the firewall to block all incoming connections, and directs the user to install updates.
- Data Execution Prevention (DEP): Support for the No Execute (NX) bit which helps to prevent buffer overflow exploits that are often the attack vector of Windows Server exploits. [4]
A full list of updates is available in the Microsoft Knowledge base here.
Service Pack 2
Service Pack 2 for Windows Server 2003 is currently under development, and has a scheduled release date for the second half of 2006.[5]
Windows Server 2003 R2
A major update of Windows Server 2003, officially called R2, also known as Windows 2003 R2 (Windows XP Server R2) (codenamed Whistler Server R2), was released to manufacturing on December 6, 2005. It is distributed as a second CD, with the first CD being Windows Server SP1. It is a new release of the server operating system.
New features
- Branch Office Server Management
- Centralized management tools for file and printers
- Enhanced Distributed File System (DFS) namespace management interface
- More-efficient WAN data replication with Remote Differential Compression
- Identity and Access Management
- Extranet Single Sign-On and identity federation
- Centralized administration of extranet application access
- Automated disabling of extranet access based on Active Directory account information
- User access logging
- Cross-platform web Single Sign-On and password synchronization using Network Information Service (NIS)
- Storage Management
- File Server Resource Manager (storage utilization reporting)
- Enhanced quota management
- File screening limits files types allowed
- Storage Manager for Storage Area Networks (SAN) (storage array configuration)
- 64-bit and .NET technologies for web performance
- Windows SharePoint Services
- ASP.NET
- IIS 6.0
- x64 support
- Server Virtualization
- A new licensing policy allows up to 4 virtual instances
- Utilities and SDK for UNIX-Based Applications add-on, giving a relatively full Unix development environment.
- Base Utilities
- SVR-5 Utilities
- Base SDK
- GNU SDK
- GNU Utilities
- UNIX Perl
- Visual Studio Debugger Add-in
Variants
This Microsoft server comes in several variants, each targeted towards a particular size and type of business: See Compare the Editions of Windows Server 2003 for a concise comparison. In general, all variants of Windows Server 2003 have the ability to share files and printers, act as an application server, and host message queues, provide email services, authenticate users, act as an X.509 certificate server, provide LDAP directory services, serve streaming media, and to perform other server-oriented functions.
Small Business Server
SBS includes Windows Server and additional technologies aimed at providing a small business with a complete technology solution. The technologies are integrated to enable small business with targeted solutions such as the Remote Web Workplace, and offer management benefits such as integrated setup, enhanced monitoring, a unified management console, and remote access.
The Standard Edition of SBS includes Windows SharePoint Services for collaboration, Microsoft Exchange Server for e-mail, Fax Server, and the Active Directory for user management. The product also provides a basic firewall, DHCP server and NAT router using either two network cards or one network card in addition to a hardware router.
The Premium Edition of SBS includes the above plus Microsoft SQL Server 2000 and Microsoft Internet Security and Acceleration Server 2004.
SBS has its own type of client access license (CAL), that is different and costs slightly more than CALs for the other editions of Windows Server 2003. However, the SBS CAL encompasses the user CALs for Windows Server, Exchange Server, SQL Server, and ISA Server, and hence is less expensive than buying all the other CALs individually.
SBS server has the following design considerations: [6]
- Only one computer in a domain can be running Windows Server 2003 for Small Business Server.
- Windows Server 2003 for Small Business Server must be the root of the Active Directory® forest.
- Windows Server 2003 for Small Business Server cannot trust any other domains.
- Windows Server 2003 for Small Business Server is limited to 75 users or devices depending on which type of CAL.
- A Windows Server 2003 for Small Business Server domain cannot have any child domains.
- Terminal Services only operates in remote administration mode on the server running SBS 2003. (Change from SBS 2000 policy)
- Each additional server must have a Windows Server 2003 for Small Business Server CAL. CALs can be employed on a per-user or per-device basis.
Web Edition
Windows Server 2003, Web Edition is mainly for building and hosting Web applications, Web pages, and XML Web Services. It is designed to be used primarily as an IIS 6.0 Web server and provides a platform for rapidly developing and deploying XML Web services and applications that use ASP.NET technology, a key part of the .NET Framework. This edition does not require Client Access Licenses and Terminal Server mode is not included on Web Edition. However, Remote Desktop for Administration is available on Windows Server 2003, Web Edition. Only 10 concurrent file-sharing connections are allowed at any moment. It is not possible to install Microsoft SQL Server and Microsoft Exchange software on this version of Windows, although MSDE and SQL Server 2005 Express are fully supported after service pack 1 is installed. The most important limitation of Web edition is a maximum memory of 2 GB RAM. Additionally, Windows Server 2003, Web Edition cannot act as a domain controller. See Compare the Editions of Windows Server 2003
Standard Edition
Windows Server 2003, Standard Edition is aimed towards small to medium sized businesses. Flexible and versatile, Standard Edition supports file and printer sharing, offers secure Internet connectivity, and allows centralized desktop application deployment. This edition of Windows will run on up to 4 processors with up to 4 GB RAM. 64-bit versions are also available for the AMD x86-64 architecture and the Intel clone of that same architecture, EM64T. The 64-bit version of Windows Server 2003, Standard Edition is capable of addressing up to 32 GB of RAM and it also supports Non-Uniform Memory Access (NUMA), something the 32-bit version does not.
Enterprise Edition
Windows Server 2003, Enterprise Edition is aimed towards medium to large businesses. It is a full-function server operating system that supports up to eight processors and provides enterprise-class features such as eight-node clustering using Microsoft Cluster Server (MSCS) software and support for up to 32 GB of memory. Enterprise Edition also comes in a 64-bit edition for Intel. 64-bit versions are also available for the AMD x86-64 architecture and the Intel clone of that same architecture, EM64T. The 64-bit version of Windows Server 2003, Enterprise Edition is capable of addressing up to 1 TB of RAM. Both 32-bit and 64-bit versions support Non-Uniform Memory Access (NUMA).
Datacenter Edition
Windows Server 2003, Datacenter Edition is designed for infrastructures demanding high security and reliability. Windows Server 2003 is available for x86 32-bit, x86 64-bit and x64 bit processors. It supports a minimum of 8 processors and a maximum of 64 processors, however it is limited to 32 processors when run on 32-bit architecture. 32-bit architecture also limits memory addressibility to 64GB, while the 64-bit versions support up to 512 GB. Windows Server 2003, Datacenter Edition, also allows limiting processor and memory usage on a per-application basis.
Windows Server 2003, Datacenter Edition also supports Non-Uniform Memory Access. If supported by the system, Windows, with help from the system firmware creates a Static Resource Affinity Table, that defines the NUMA topology of the system. Windows then uses this table to optimize memory accesses, and provide NUMA awareness to applications, thereby increasing the efficiency of thread scheduling and memory management.
Windows Server 2003, Datacenter edition has better supports for Storage Area Networks (SAN). It features a service which uses Windows sockets to emulate TCP/IP communication over native SAN service providers, thereby allowing a SAN to be accessed over any TCP/IP channel. With this, any application that can communicate over TCP/IP can use a SAN, without any modification to the application.
Windows Server 2003, Datacenter edition, also supports 8-node clustering. Clustering increases availability and fault tolerance of server installations, by distributing and replicating the service among many servers. Windows supports clustering, with each cluster having its own dedicated storage, or all clusters connected to a common Storage Area Network (SAN), which can be running on Windows as well as non-Windows Operating systems. The SAN may be connected to other computers as well.
Compute Cluster Server
Template:Expandsect Windows Compute Cluster Server 2003 is designed for working with demanding problems in computing, that requires high performance computing clusters. Compute Cluster edition deploys in clusters of multiple servers to form large supercomputers. Microsoft intends to release this edition in 2006.
Storage Server
Windows Storage Server 2003, a part of the Windows Server 2003 series is a specialized server operating system for Network Attached Storage (NAS). It is optimized for use in file and print sharing and also in Storage Area Network (SAN) scenarios. It is only available through OEMs, with Network Attached Storage (NAS) devices, with capacities in excess of a few terabytes. Unlike other Windows Server 2003 editions that provide file and printer sharing functionality, Windows Storage Server 2003 does not require any Client access licenses.
Windows Storage Server 2003 NAS equipments are headless, which means that they are without any monitors, keyboards or mice, and are administered remotely. Such devices are plugged into any existing IP network and the storage capacity is available to all users. Using NAS devices means that data is decentralized and shared amongst all users of the network, even though access through the data can be controlled. Windows Storage Server 2003 can use RAID arrays to provide redundancy, fault-tolerance and high-performance. Multiple such NAS servers can be clustered to appear as a single device. This allows for very high performance as well as it allows the service to remain up even if one of the servers goes down.
Windows Storage Server 2003 can also be used to create a Storage Area Network, in which the data is transferred in terms of chunks rather than files, thus providing more granularity to the data that can be transferred. This provides higher performance to database and transaction processing applications. Windows Storage Server 2003 also allows NAS devices to be connected to a SAN.
Windows Storage Server 2003 R2, as a follow-up to Windows Storage Server 2003, adds file-server performance optimization, Single Instance Storage (SIS), and index-based search. Single instance storage(SIS) scans storage volumes for duplicate files, and moves the duplicate files to the common SIS store. then moves duplicates to the SIS common store. The file on the volume is replaced with a link to the file. This substitution reduces the amount of storage space required, by as much as 70%
Windows Storage Server R2 provides an index-based, full-text search based on the indexing engine already built-in Windows server. The updated search engine speeds up indexed searches on network shares. Storage Server R2 also provides filters for searching many standard file formats, such as .zip, AutoCAD, XML, MP3, and .pdf, and all Microsoft Office file formats.
Windows Storage Server 2003 R2 includes built in support for Windows SharePoint Services and Microsoft SharePoint Portal Server, and adds Storage Management snap-in for the Microsoft Management Console. It can be used to centrally manage storage volumes, including DFS shares, on servers running Windows Storage Server R2.
Windows Storage Server R2 cannot be used as an iSCSI target, but can be an iSCSI initiator. This deficiency is slated to be addressed in an upcoming release of Windows Storage Server.
Features
- Distributed File System (DFS): DFS allows multiple Network Shares to be aggregated as a virtual file system.
- Support for SAN and iSCSI: Computers can connect to a Storage Server over the LAN, and there is no need for a separate fibre channel network. Thus a Storage Area Network can be created over the LAN itself. iSCSI uses the SCSI protocol to transfer data as a block of bytes, rather than as a file. This increases performance of the Storage network in some scenarios, such as using a database server.
- Virtual Disc Service: It allows NAS devices, RAID devices and SAN shares to be exposed and managed as if they were normal hard drives.
- JBOD systems: JBOD (Just a bunch of discs) systems, by using VDS, can manage a group of individual storage devices as a single unit. There is no need for the storage units to be of the same make and model.
- Software and Hardware RAID: Windows Storage Server 2003 as intrinsic support for hardware implementation of RAID. In case hardware support is not available, it can use software enabled RAID. In that case, all processing is done by the OS.
- Multi Path IO (MPIO): It provides an alternate connection to IO devices in case the primary path is down.
Pricing
Small Business Server: Average cost is $599 USD, the product is purchased through a brick-and-mortar retailer, while an open new license must be purchased through a volume license reseller.
Web Edition: This operating system is priced at $397 USD. Client Access Licenses are not required.
Standard Edition: This operating system is priced at $999 USD, although licences may be purchased for less from a reseller. For more than 5 Active Directory remote-connected users (users of Exchange, for example) additional costs are incurred.
Enterprise Edition: This operating system is priced at $3,999 USD. For more than 25 remote-connected users, additional costs are incurred (either CALs or the EC license).
Datacenter Edition: This operating system’s price is unknown, since it must be obtained through an OEM.
Compute Cluster Edition: This operating system’s price is unknown, since it is yet to be released in January 2006.
Storage Server: This operating system’s price is unknown, since it must be obtained through an OEM. It is rumored to cost between $500 and $1000.
External Connector: an additional license required when non-employees authenticate to Windows applications, for example on an internet-connected application server. Priced at $3999 USD per server.
All these prices are estimated retail; actual prices will vary depending on the reseller.