Создаём загрузочный USB диск с Windows из под Linux
В ubuntu уже есть приложение для создания образов дисков — Startup Disk Creator, но оно умеет создавать только загрузочные USB с Linux. Для создания загрузочного USB-диска с Windows из Linux, существует WinUSB, но она довольно давно не обновлялась, и честно говоря, у меня не заработала. Данный пост довольно подробный, и рассчитан преимущественно на людей, плохо знакомых с Linux.
Перед тем как я продолжу, следует указать что в Windows мире два метода загрузки:
- MBR, при котором в начале диска резервируется место, и располагается специальный загрузочный файл;
- EFI, при котором исполняемый файл загрузчика хранится в стандартном расположении на FAT32 файловой системе;
Если вы не знаете какой выбрать, то наиболее часто используемый вариант который работает без модификации файлов Windows — это msdos таблица разделов с fat32 файловой системой и загрузочным флагом.
Прежде всего USB-диск необходимо подготовить. В Linux наиболее простой и удобной для этих целей утилитой является gparted.
Ставим его если не установлен:
Подготовка USB диска
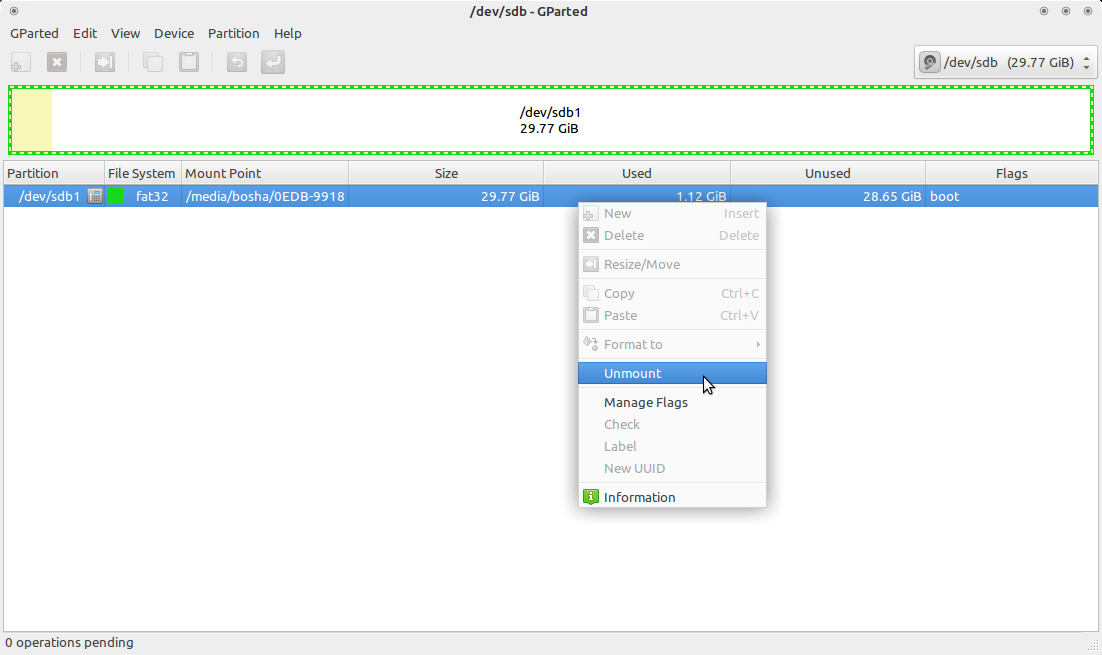
Выбираем нашу USB флэшку, отмонтируем её если она смонтирована:
Отмонтирование USB диска в gparted
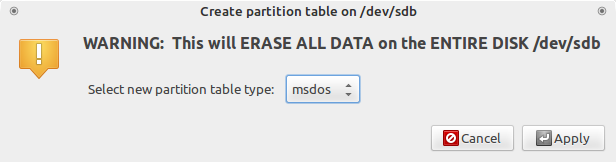
Теперь необходимо пересоздать таблицу разделов, при этом выбрать тип msdos . Заходим в меню Устройство (Device) и выбираем Создать таблицу разделов (Create partition table) :
Gparted создание таблицы разделов
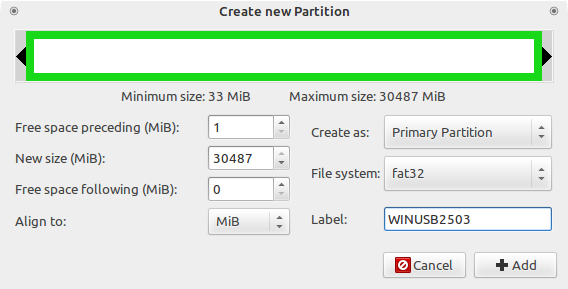
После этого выбираем неразмеченную область, нажимаем правой кнопкой мыши по ней же и выбираем пункт меню «Новый». В появившемся окне выбираем файловую систему NTFS или FAT32. Если у вас какая-то нестандартная сборка в которой могут быть файлы больше 4 гигабайт, то файловая система должна быть определенно NTFS, в противном случае, можно выбрать FAT32, и, тогда, так же можно будет загрузиться с UEFI. Так же необходимо указать метку для USB-диска. Важно: метка должна быть не просто «Windows», а какой либо более уникальной. Если файловая система FAT32, то метка должна быть указана заглавными буквами.
Создание нового раздела Gparted
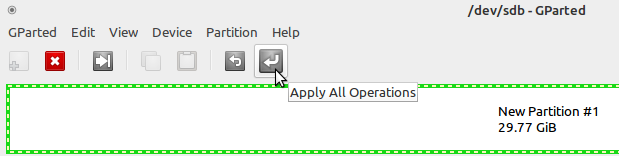
Применяем все наши изменения:
Применение изменений в Gparted
Выходим из gparted.
Копирование файлов Windows на USB диск
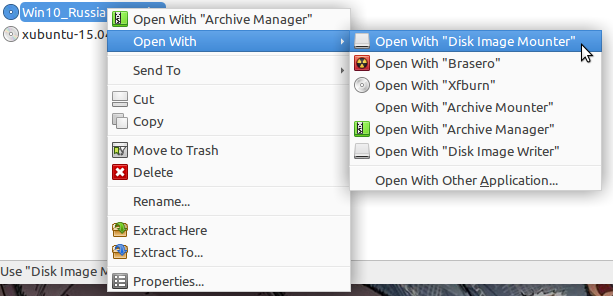
Теперь необходимо смонтировать образ с Windows и скопировать данные с него на наш подготовленный ранее usb диск. В большинстве современных рабочих окружений это можно сделать из файлового менеджера. По необходимому образу нажимаем правой кнопкой мыши, выбираем Открыть с помощью и выбираем Disk Image Mounter :
Монтирование образа с Windows в файлом менеджере Thunar
Если у вас нет такой утилиты, то можно смонтировать из командной строки:
Где $HOME/Загрузки/Windows.iso необходимо заменить на путь до образа с Windows. Образ будет смонтирован в директорию /mnt/cdrom .
Делаем USB-диск загрузочным
Если создаем MBR загрузочный диск
Для создания MBR загрузочной записи будем использовать grub:
- $user — имя текущего пользователя;
- $drive — название образа;
- /dev/sdX — расположение диска (в моем случае /dev/sdb ;
Если образ монтировали руками, то /media/$user/$drive/boot необходимо заменить на /mnt/cdrom/boot .
В случае, если не было никаких ошибок, то в консоли должны увидеть примерно следующее:
Теперь на USB-диске в директории boot/grub необходимо создать файл grub.cfg с таким содержимым:
В листинге выше, $USB_drive_label необходимо заменить на метку, которую мы присвоили диску на первом шаге. В данном случае WINUSB2503 .
Перезагружаемся, загружаемся с USB-диска и выбираем Start Windows Installation .
Если создаем UEFI загрузочный диск
С UEFI все несколько проще. Следует обратить внимание, что данный способ подходит только для Windows 7 x64 и выше.
После того, как все файлы скопировались, необходимо зайти в директорию efi/boot . Если в ней присутствуют файлы bootx64.efi или bootia32.efi то всё в порядке, можно пробовать загрузиться с диска.
Ubuntu Documentation
Outline
The general procedure to install Ubuntu (or Ubuntu flavour, Kubuntu, Lubuntu, Xubuntu, . ) from a USB flash drive is:
Get the correct Ubuntu installation file, ‘the iso file’, via this link or Ubuntu flavour via this link. Download the iso file into your running computer (for example into the directory Downloads in the internal drive, not into the USB flash drive that you want to make into a USB boot drive).
Check with md5sum (or another checksum tool) that the download was good.
Try Ubuntu (Kubuntu, Lubuntu, Xubuntu, . ) before installing it.
See also: Installation/FromUSBStickQuick for beginners starting from Windows.
Introduction
Ubuntu can be installed from a USB flash drive. This may be necessary for most new portable computers without DVD drives and is handy for others because a USB flash drive is so convenient. Also, you can configure Ubuntu on the USB flash drive to save changes you make, unlike a read-only CD/DVD disk.
Booting from a USB flash drive created with usb-creator alias Startup Disk Creator and mkusb will behave just as if you had booted from the install CD. It will show the language selection and then the install menu, from which you can install Ubuntu onto the computer’s hard drive or launch the LiveCD environment. Other utilities, e.g. UNetbootin, may create slightly different boot drives or if on UEFI might not work at all with Debian iso files due to a bug
Note: This article uses the term «USB flash drive» alongside USB stick, USB drive, USB device, USB pendrive and thumb drive.
Prerequisites
To create a USB installation device, you will need:
a 4 GB USB flash device/drive/stick. If the iso file is smaller than 2 GB, it is possible to use a 2 GB USB device, at least with some of the methods. Files on this USB device will be erased, so backup the files you want to keep before making the device bootable. Some of the tools require that this USB device is properly formatted and mounted while other tools will overwrite whatever is on the target device. Please follow the instructions for each tool.
an Ubuntu flavour ISO file downloaded from an official web page, ubuntu.com/download or http://releases.ubuntu.com, stored in your running computer (for example in the directory Downloads in the internal drive, not in the USB flash drive that you want to make into a USB boot drive).
Check with md5sum (or another checksum tool) that the download was good. In Linux there is the tool ‘md5sum’. In Windows you can do it with Rufus: click on the circle with a tick mark (more about Rufus here.)
Dummy headlines
After a major remake of this help page the following headlines are kept here because they may be linked to from other web sites. Several other headlines further down in the page are also kept for this reason.
Notes about speed
Notes about size
Notes about bootability
The flash hardware
There is a detailed description at the sub-page /pre
Creating a bootable Ubuntu USB flash drive from Windows
There are various methods available for Windows to create a bootable Ubuntu USB flash drive.
NEVER try to use one of your hard disk drives or partitions in this process unless you really know what you are doing, as data will get erased.
Rufus
Rufus is the tool in Windows that is recommended officially by Ubuntu. A tutorial is available from here.
balenaEtcher
Pendrivelinux’s Universal USB Installer
UNetbootin
Win32 Disk Imager
There is a detailed description at /fromWindows including Rufus, balena Etcher, Universal USB Installer, Unetbootin and Win32 Disk Imager.